No edit summary |
(同步 english) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
[[Image:Artwork_DesignService_fedora-iso-usb.png|right]] | [[Image:Artwork_DesignService_fedora-iso-usb.png|right]] | ||
本页介绍 '''如何创建并使用 Fedora 启动 U 盘'''。您可以将 [https://getfedora.org/ Fedora ISO 镜像] 写入 U 盘,在不安装 Fedora 系统到硬盘的情况下启动一台支持 U 盘启动的电脑。您可以在启动U盘中划分一块区域存储对系统的更改(安装软件或修改配置),这种模式称为 '''持续覆盖'''。您也可以划分一块单独空间用来存储用户账户信息和数据,比如文档和下载的文件,当然,为了数据安全您可以选择加密它们。总之,因为安装是非破坏性的,之前的文件和剩余的空间都可以在系统中访问。这相当于把整个电脑装在口袋里,在能找到的大部分机器上启动您自己的系统。 | |||
在现在的 Fedora 版本中,您也可以把非 Live 版本的 Fedora 镜像(DVD 和网络安装镜像)写入 U 盘,这样比写入光盘更快更方便。 | |||
{{anchor|quickstarts}} | |||
{{anchor|fmw}} | |||
{{anchor|luc}} | |||
== 快速开始:使用 Fedora Media Writer == | |||
[[Image:Fedora_Live_USB_creator.png|thumb|right|Fedora Media Writer 截图]] | |||
在大多数情况下,创建 Fedora U 盘的最佳工具是 [https://github.com/MartinBriza/MediaWriter Fedora Media Writer],以前称为 [http://fedorahosted.org/liveusb-creator LiveUSB Creator]。它目前支持 Fedora(其他发行版使用 [http://flatpak.org/ Flatpak]),Windows 和 macOS。 | |||
{{admon/important | 破坏性方法 | 该方法将破坏 USB 存储设备中的所有数据。如果您需要非破坏性写入方法(以保留 U 盘上的现有数据)或支持 '持久化数据',您应该使用 [[#litd|livecd-iso-to-disk]] 实用工具。}} | |||
Fedora Media Writer 图形化工具非常易于使用。它可以下载最新版本的 Fedora 镜像,并将其写入 U 盘。 | |||
在 Fedora 中,您可以使用图形化软件安装工具安装 {{package|mediawriter}} 包,或使用以下命令安装: | |||
<pre> | |||
su -c 'dnf --enablerepo=updates-testing install mediawriter' | |||
</pre> | |||
在 Windows 和 macOS 中,您可以从 [https://github.com/MartinBriza/MediaWriter/releases 发布页] 下载安装包。在其他 Linux 发行版,如果支持 [http://flatpak.org/ Flatpak] 应用分发系统,您可以从 [https://github.com/MartinBriza/MediaWriter/releases 发布页] 下载 flatpkg 包。 | |||
要运行该工具,请在系统菜单中查找 '''Fedora Media Writer'''。当您启动 Fedora Media Writer 时,底部的三个点将闪烁,工具将检查新的 Fedora 版本。 | |||
执行以下步骤写入 U 盘: | |||
# 选择您希望安装或试用的 Fedora 版本。 | |||
#: 在标题页,您可以选择 Workstation, Server 或您的 .iso 文件。其他选项(包括 KDE, Cinnamon, Xfce 等等)在列表底部的 "..." 按钮中。 | |||
# 确保您的 U 盘已插入系统。 | |||
# 点击 ''Create Live USB''。 | |||
# 确保已选择右侧的 U 盘。 | |||
# 点击 ''Write to disk'' 并等待写入完成。 | |||
# 一旦写入完成,关闭系统并从 U 盘启动(参见 [[#booting|引导部分]])。 | |||
写入后,您的 U 盘分区布局将改变,一些系统可能提示它有 10MB 容量。要将 U 盘恢复出厂设置,请在 Fedora Media Writer 运行时再次插入 U 盘。应用程序将提供恢复出厂设置的选项。恢复后,U 盘将包含一个 VFAT 分区。 | |||
__TOC__ | |||
= | = 系统需求 = | ||
* 一台使用 GNU/Linux,Windows 或者 MacOS 的电脑。 | |||
* 一个拥有 1G 以上存储空间的 [[wikipedia:USB flash drive|USB闪存设备]],比如 U 盘、存储卡等 。 | |||
* 1 个从 http://fedoraproject.org/get-fedora 下载的镜像文件。 | |||
{{anchor|booting}} | |||
== 从 USB 设备启动 == | |||
[[Image:Bios_USB_boot.jpg|thumb|right|设置 USB 为第一引导设备。您的 BIOS 可能略有不同。]] | |||
几乎所有的现代 PC 都支持从 U 盘启动(有些非常老的可能无法启动)。当然,您需要设置从 USB 引导启动系统。首先,您需要按以下步骤操作: | |||
# 关闭计算机。 | |||
# 插入 USB 设备。 | |||
# 移除所有其他便携式媒体,例如 CD, DVD, 软盘或其他 U 盘。 | |||
# 启动计算机。 | |||
# 如果计算机配置为从 USB 驱动器自动引导,您将看到屏幕显示 "Automatic boot in 10 seconds..."(如果您的计算机支持 UEFI 引导,这里会显示更多的 最小启动菜单)。 | |||
如果计算机正常从硬盘驱动器引导,您需要手动配置 BIOS 从 U 盘驱动器引导。通常,应该按以下步骤操作: | |||
# 等待计算机安全重启。 | |||
# 当计算机开始重启时,您需要仔细观察并按下指定按键(通常是 Escape, Tab, F12 或 Delete)进入引导设备选择菜单。如果您错过了,需要重启并重试。 | |||
# 进入 "BIOS" 或引导设备选择菜单,将您的 USB 设备设为第一启动项。 | |||
#: '''注意!''' 如果您修改了其他设置,可能会导致计算机无法启动。建议您记住修改的选项,以备不时之需。 | |||
# 保存更改,退出,从 USB 设备引导启动计算机。 | |||
如果您的系统基于 [[Unified_Extensible_Firmware_Interface|UEFI]] 固件,它通常支持 UEFI 模式和 BIOS 兼容模式。如果您以 UEFI 模式启动并安装 Fedora,Fedora 引导将安装至 UEFI 分区(以 UEFI+GPT 模式启动)。如果您以 BIOS 兼容模式启动并安装 Fedora,Fedora 将以 BIOS+MBR 模式启动。更多信息,请参阅 [[Unified_Extensible_Firmware_Interface|UEFI 页]]。使用 [[#fmw|Fedora Media Writer]], [[#gnome|GNOME Disk Utility]], [[#dd|dd]], 或其他类似 dd 的工具,和 [[#litd|livecd-iso-to-disk]] 的 {{code|--efi}} 选项将 x86_64 镜像写入 U 盘,U 盘将支持 UEFI 引导。使用其他工具写入 U 盘可能不支持 UEFI 引导,并且 i686 镜像不支持通过 UEFI 引导。 | |||
== 检查 USB 磁盘大小 / 可用空间 == | |||
/ | |||
如前所述,磁盘必须有一定的存储空间,具体取决于您选择的镜像。如果您使用破坏性方法,U 盘必须至少为镜像大小;如果使用非破坏性方法,它必须至少有足够的可用空间。无论您使用什么操作系统,都可以通过文件管理器检查设备可用空间,通常是右键单击并选择 ''Properties''。以下是 GNOME 文件管理器截图: | |||
[[image:Properties_USB_size.png]] | [[image:Properties_USB_size.png]] | ||
您也可以通过执行 {{command|df -h}} 命令查看: | |||
<pre> | |||
/dev/sdX1 3.9G 4.0K 3.9G 1% /media/usbdisk | |||
</pre> | |||
确保第一栏大于 1.0G。 | |||
== | {{anchor|#device}} | ||
{{anchor|device}} | |||
== 在 Linux 上通过 {{filename|/dev}} 名称标识设备 == | |||
[[ | 大多数 [[#writing|其他写入方法]] 都需要知道 U 盘的 {{filename|/dev}} 设备名称。例如,当使用 Linux 时可能为 {{filename|/dev/sdc}}。[[#fmw|Fedora Media Writer]] 不需要用户提供设备名。查找设备名可使用以下步骤: | ||
# 插入 U 盘。 | |||
# 打开终端,运行 {{command|dmesg|grep removable}}。 | |||
# 在输出的最后,您会看到类似的信息: | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
[32656.573467] sd 8:0:0:0: [sdX] Attached SCSI removable disk | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
其中 sdX(可能是 sdb, sdc, sdd等)标签就是您需要使用的设备名。如果您连接了多个 USB 设备,请'''务必'''小心识别设备名,通常输出中会包含制造商名称或容量,可以使用这些来区分多个 USB 设备。'''记下这个标签''',下文我们称之为 ''sdX''。 | |||
{{anchor|writing}} | |||
== 其他 U 盘写入方法 == | |||
在大多数情况下,推荐使用 [[#fmw|Fedora Media Writer]]。在本节中,记录了其他有用的工具。 | |||
=== | {{anchor|gnome}} | ||
=== 使用 GNOME Disk Utility (Linux, 图形, 破坏性) === | |||
{{admon/ | {{admon/important | 破坏性方法 | 该方法会破坏 U 盘中的所有数据。如果您需要非破坏性方法(保留 U 盘中的数据)或需要 '持久化数据',您需要使用 [[#litd|livecd-iso-to-disk]]。}} | ||
此方法适用于已安装 GNOME,Nautilus 和 GNOME Disk Utility 的 Linux(或 *nix)。如果您使用的是不支持 Flatpak 的发行版,这可能是最简单的方法。标准安装的 Fedora 或许多其他基于 GNOME 的发行版,都可以使用此方法。在 Fedora 上,确保已安装 {{package|nautilus}} 和 {{package|gnome-disk-utility}} 软件包。也可以使用其他桌面环境的图形化写入工具,或使用 [[#dd|命令行"直接写入"方法]]。 | |||
# 下载 Fedora 镜像,插入不包含任何有用数据的 U 盘 | |||
# 运行 Nautilus (Files) | |||
# 找到已下载的镜像,右键单击,转到'''Open With''',并点击 '''Disk Image Writer''' | |||
# 再次检查 U 盘,确保您真的不需要其中的数据! | |||
# 在 '''Destination''' 中选择您的 U 盘,并点击 '''Start Restoring...''' | |||
{{anchor|litd}} | |||
=== 命令行方法:使用 ''livecd-iso-to-disk'' 工具 (仅 Fedora, 非图形, 破坏性/非破坏性) === | |||
{{admon/ | {{admon/important | 潜在破坏性方法 | ''如果使用 '''--format''' 参数'',该方法将破坏 U 盘中的所有数据。}} | ||
{{command|livecd-iso-to-disk}} 方法的可靠性比 Fedora Media Writer 稍差,只能在 Fedora 中可靠地使用:它不能在 Windows 或 macOS 中使用,且不支持(通常失败)非 Fedora 发行版。但是,它支持 FMW 不支持的三个高级功能: | |||
# 您可以使用 ''非破坏性'' 方法创建安装 U 盘,U 盘中的现有文件不会被销毁。该方法没有 ''破坏性 '' 写入方法可靠,且只在没有 U 盘可用时才使用。 | |||
# 写入 Live 镜像时,您可以使用 ''永久覆盖'' 功能,它允许在重启后保留之前的更改。您可以定期执行更新,就像使用磁盘中的系统一样。当然,内核更新需要 [[#Kernel updates|手动介入]];另外,[[#limited overlay|覆盖空间可能不足]]。不使用 ''永久覆盖'' 功能,每次启动时将丢弃之前的更改。 | |||
# 在 Live 镜像上,您也可以划分一个独立的区域来存储用户账户信息和数据,例如文档和下载的文件,可选的加密让您的数据更安全。 | |||
通过结合这些功能,您可以随身携带您的 Fedora 系统,并在任何计算机中启动。 | |||
在旧的 Fedora 系统中使用 {{command|livecd-iso-to-disk}} 写入新系统不是个好主意: | |||
最好只写入一个版本,最多覆盖旧版本不超过两次。 | |||
请确保已安装 {{package|livecd-tools}} 软件包:{{command|su -c 'dnf install livecd-tools'}} | |||
基本示例如下。请注意首先[[#device|识别您的 U 盘设备名]]。在所有情况下,您可以添加参数{{command|--efi}}(尝试)以原生 UEFI 模式制作引导 U 盘。更详细的使用信息,请运行:{{command|livecd-iso-to-disk --help}} 或 {{command|man livecd-iso-to-disk}}。 | |||
要将现有的 U 盘制作为可启动 U 盘,而不删除其中的任何数据,请确保在执行以下操作前未挂载 USB 驱动器,并在出现提示时输入 root 密码: | |||
: {{command|su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-{{FedoraVersionNumber|next}}-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"}} | |||
如果无法从使用上述方法创建的磁盘进行引导,则在重新分区和格式化前,重置为主引导记录: | |||
: {{command|su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk --reset-mbr Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-{{FedoraVersionNumber|next}}-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"}} | |||
{{admon/warning | 小心: | 在以下命令中使用 {{command|--format}} 选项,将擦除 USB 驱动器中的所有数据!请''仔细''阅读下面的说明。}} | |||
如果有必要,您可以使用 ''livecd-iso-to-disk'' 重新分区和格式化目标设备: | |||
: {{command|su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk --format --reset-mbr Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-{{FedoraVersionNumber|next}}-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"}} | |||
使用 {{command|--home-size-mb}} 参数,可以为 {{filename|/home}} 划分保留的文件系统。例如: | |||
: {{command|su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk --home-size-mb 2048 Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-{{FedoraVersionNumber|next}}-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"}} | |||
这将创建一个 2GiB 文件系统,每次启动 U 盘时挂载为 {{filename|/home}},从而允许您保留 {{filename|/home}} 中的数据。 | |||
要启用 '数据持久性' 支持(对整个 Live 环境所做的更改将在引导期间持续存在),需要添加 {{command|--overlay-size-mb}} 参数,将持久性数据存储区域添加到目标设备。例如: | |||
{{command|su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk -- | : {{command|su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk --overlay-size-mb 2048 Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-{{FedoraVersionNumber|next}}-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"}} | ||
其中 2048 是覆盖的期望大小(MB)。对于 VFAT,''livecd-iso-to-disk'' 工具不接受大于 4095 的值;对于 ext[234] 文件系统,只受可用空间的限制。 | |||
{{anchor|limited overlay}} | |||
{{admon/note | 持续覆盖的限制 | 由于目前的实现方式,对于持续覆盖的每次修改(写入和删除)都会占用它的可用空间,所以空间最终会被“用尽”,您的 U 盘将不能再启动(参见 [http://thread.gmane.org/gmane.linux.kernel.device-mapper.devel/14644 dm-devel 讨论] 和 [[LiveOS_image#Overlay_recovery|紧急恢复]])。您可以使用 {{command|dmsetup status live-rw}} 查看叠加层中剩余的空间:输出类似于 {{code|snapshot 42296/204800}},表示总共 204800 个 512 字节扇区,已消耗 42486 个。由于这些限制,建议谨慎使用系统级持久覆盖,仅进行配置更改和重要的安全更新。或者,如果有足够的可用磁盘空间,可以将 LiveOS 根文件系统快照的更改合并到新副本中。有关说明,请参阅 [[LiveOS image#Merge overlay into new image|该页面]]。}} | |||
您可以组合 {{command|--home-size-mb}} 和 {{command|--overlay-size-mb}},这种情况下写入 {{filename|/home}} 的数据不会占用持久覆盖的空间。 | |||
{{anchor|dd}} | |||
=== 命令行 "直接写入" 方法 (多操作系统, 非图形, 破坏性) === | |||
{{admon/important | 破坏性方法 | 该方法会破坏 U 盘中的所有数据。如果您需要非破坏性方法(保留 U 盘中的数据)或需要 '持久化数据',您需要使用 [[#litd|livecd-iso-to-disk]]。}} | |||
此方法直接将镜像写入 U 盘,就像 [[#fmw|Fedora Media Writer]] 或 [[#gnome|GNOME Disk Utility]],但使用名为 {{command|dd}} 的命令行工具。与其他 “直接写入” 方法一样,它会破坏 U 盘中的所有数据,不支持任何高级功能,如数据持久性,但该方法非常可靠。 {{command|dd}} 工具可用于大多数类 Unix 操作系统,包括 Linux 和 macOS,以及 [http://www.chrysocome.net/dd 一个 Windows 版本]。如果您不能使用 Fedora Media Writer 或 GNOME 磁盘实用程序,或只是喜欢命令行程序,并想要一个简单/快速的方式写入 U 盘,这就是最好的方法。 | |||
# [[#device|识别您的 U 盘设备名]]。如果您使用 Windows,{{command|dd --list}} 命令将显示正确的名称。 | |||
# '''卸载该设备所有已挂载的分区。''' 这非常重要,否则写入的镜像可能损坏。您可以使用 {{command|umount /dev/sdX*}} 命令卸载所有分区。 | |||
# 将 ISO 文件写入设备: | |||
#: {{command|1=su -c 'dd if=/path/to/image.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=8M status=progress oflag=direct'}} | |||
# 等待命令完成。 | |||
#: 如果您看到 {{code|dd: invalid status flag: 'progress'}},您的 dd 版本不支持 {{code|1=status=progress}} 选项,您需要删除该选项,然后重试(您将不能看到进度条)。 | |||
{{anchor|unetbootin}} | |||
=== 使用 [http://unetbootin.sourceforge.net/ UNetbootin] (Windows, macOS 和 Linux, 图形, 非破坏性) === | |||
[[Image:Unetbootin_gtk3.png|thumb|right|Unetbootin 截图]] | |||
{{admon/warning | 可靠性未知 | 每次发布版本,Fedora 的志愿者都会收到使用 UNetbootin 创建安装镜像的问题报告。使用最新版本的 UNetbootin 可以避免一些问题。UNetbootin 可以在某些情况下工作,但不能在其他情况下工作。例如,它会创建一个 BIOS 模式下可引导的 U 盘,但不支持 UEFI 模式。Fedora 不能保证支持 UNetbootin 写入的镜像。}} | |||
虽然结果可能会有所不同,但通常情况下,使用 [[#fmw|Fedora Media Writer]], [[#litd|livecd-iso-to-disk]], [[#gnome|GNOME]] 和 [[#dd|dd]] 方法的结果比 UNetbootin 更好。如果您遇到 UNetbootin 的问题,请联系 UNetbootin 开发人员。 | |||
UNetbootin 是一个图形化的可引导 U 盘镜像写入工具。它允许您保存 USB 驱动器中的任何数据。如果您在启动时遇到问题,可以尝试使用一个干净的 FAT32 格式的驱动器。 | |||
如果您运行的是 64 位 Linux 发行版,UNetbootin 可能无法运行,您需要安装相当多的 32 位系统库。Fedora 无法帮助您:请直接向 UNetbootin 开发人员反馈问题。 | |||
[ | # 从 [http://unetbootin.sourceforge.net/ UNetbootin 官方网站] 下载最新版本,并安装。在 Linux 中,下载可执行文件,添加可执行权限 {{command|chmod ugo+x filename}},运行即可。 | ||
# 启动 UNetbootin。在 Linux 中,需要输入 root 密码。 | |||
# 点击 '''Diskimage''',并选择您下载的 ISO 文件。 | |||
# 选择类型:USB 设备和 [[#device|选择正确的 USB 设备]] | |||
# 点击确定 | |||
{{admon/note | 设备不可见 | 如果您未看到 ''sdX'',您可能需要重新格式化设备。您可以使用大多数文件管理器或磁盘实用工具,例如,GNOME disk utility。建议使用 FAT32 格式。这会丢失您驱动器中的所有数据。}} | |||
=== 从运行的 Live 环境创建安装 U 盘 === | |||
如果您已运行在 Live CD, DVD, USB 环境。您可以执行以下命令,制作一个可引导 U 盘。 | |||
: {{command|su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk /run/initramfs/livedev /dev/sdX"}} | |||
在外部挂载根文件系统,请参阅 [[#Mounting a Live USB filesystem|该节]]。 | |||
[[ | |||
= | == 故障排除 == | ||
== | === Fedora Media Writer 问题 === | ||
* | * 可以向 [https://github.com/MartinBriza/MediaWriter/issues GitHub] 或 [https://bugzilla.redhat.com/enter_bug.cgi?product=Fedora&component=mediawriter Bugzilla] 提交错误报告。 | ||
* 您可以 [http://bugz.fedoraproject.org/mediawriter 浏览已存在的 Bugzilla 报告]。 | |||
* | |||
=== | === livecd-iso-to-disk 问题 === | ||
==== 分区未标记为可引导! ==== | |||
如果您收到消息 {{code|Partition isn't marked bootable!}},您需要标记分区为可引导。为此,运行 {{command|su -c 'parted /dev/sdX'}},并使用 {{code|toggle N boot}} 命令(N 为分区号)。例如: | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
$ parted /dev/ | $ parted /dev/sdb | ||
GNU Parted 1.8.6 | GNU Parted 1.8.6 | ||
Using /dev/ | Using /dev/sdb | ||
Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands. | Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands. | ||
(parted) print | (parted) print # 查看分区信息 | ||
Model: Imation Flash Drive (scsi) | Model: Imation Flash Drive (scsi) | ||
Disk /dev/sdX: 1062MB | Disk /dev/sdX: 1062MB | ||
| Line 239: | Line 232: | ||
1 32.3kB 1062MB 1062MB primary fat16 | 1 32.3kB 1062MB 1062MB primary fat16 | ||
(parted) toggle 1 boot | (parted) toggle 1 boot # 标记分区1 为可引导 | ||
(parted) print | (parted) print # 查看分区信息 | ||
Model: Imation Flash Drive (scsi) | Model: Imation Flash Drive (scsi) | ||
Disk /dev/sdX: 1062MB | Disk /dev/sdX: 1062MB | ||
| Line 249: | Line 242: | ||
1 32.3kB 1062MB 1062MB primary fat16 boot | 1 32.3kB 1062MB 1062MB primary fat16 boot | ||
(parted) quit | (parted) quit # 退出 | ||
Information: Don't forget to update /etc/fstab, if necessary. | Information: Don't forget to update /etc/fstab, if necessary. | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
=== | ==== 分区需要文件系统标签! ==== | ||
如果您收到消息 {{code|Need to have a filesystem label or UUID for your USB device}},您需要为分区设置标签:{{command|su -c "dosfslabel /dev/sdX LIVE"}} | |||
Need to have a filesystem label or UUID for your USB device | |||
==== 分区有不同的物理/逻辑结束标记! ==== | |||
如果您从 fdisk 获得该消息,您需要在写入镜像时,使用 {{code|--format}} 参数重新格式化 U 盘。 | |||
==== MBR 显示为空白! ==== | |||
如果测试引导报告损坏的引导扇区,或者您收到消息 {{code|MBR appears to be blank.}},您需要在写入镜像时,使用 {{code|--reset-mbr}} 选项重设主引导记录(MBR)。 | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
$ su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk Fedora- | $ su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-{{FedoraVersionNumber|next}}-1.1.iso /dev/sdX" | ||
MBR appears to be blank. | MBR appears to be blank. | ||
You can add an MBR to this device with | You can add an MBR to this device with | ||
| Line 282: | Line 265: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
重设主引导记录(MBR): | |||
<pre> | |||
$ su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk --reset-mbr Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-{{FedoraVersionNumber|next}}-1.1.iso /dev/sdX" | |||
</pre> | |||
== | ==== 在其他 Linux 发行版使用 livecd-iso-to-disk ==== | ||
{{command|livecd-iso-to-disk}} 不能在非 Fedora 系统中运行。即使它在其他发行版可以运行并成功写入 U 盘,该 U 盘也可能无法引导。在其他非 Fedora 发行版上使用 {{command|livecd-iso-to-disk}} 不受支持,无法正常工作:请使用其他方法,例如 [[#fmw|Fedora Media Writer]]。 | |||
= | === Ubuntu 的 ''usb-creator'' 命令 === | ||
Ubuntu 及其衍生版有一个 {{command|usb-creator}} 程序,类似于 Fedora Media Writer。它'''不能'''用于写入 Fedora ISO 镜像。usb-creator 需要 ISO 具有 Debian 布局,具有 {{filename|/.disk/info}} 文件和 casper 目录。不要尝试使用该工具写入 Fedora ISO 镜像。 | |||
== 使用 qemu 测试可引导 U 盘 == | |||
以下截图展示了,使用 QEMU 测试可引导 U 盘。 | |||
[[Image:Screenshot_qemu_gtk3.png|thumb]] | [[Image:Screenshot_qemu_gtk3.png|thumb]] | ||
例如,使用以下命令测试可引导 U 盘: | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
su -c 'umount /dev/sdX1' | su -c 'umount /dev/sdX1' | ||
qemu -hda /dev/sdX -m 1024 -vga std | qemu -hda /dev/sdX -m 1024 -vga std | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
== 挂载 Live USB 文件系统 == | |||
您可以尝试使用 {{package|livecd-tools}} 包中的 [https://github.com/rhinstaller/livecd-tools/blob/master/tools/liveimage-mount ''liveimage-mount''] 脚本,来挂载 Live USB 设备或其他 LiveOS 镜像,例如 ISO 或 Live CD。 | |||
当您需要在 Live USB 上的 Live 文件系统中复制某些文件,或查看 Live ISO 或 Live CD 中的文件时,使用该脚本很方便。 | |||
== 为使用 ''livecd-iso-to-disk'' 持久覆盖模式写入的镜像更新内核 == | |||
如果您的 U 盘有 [[#limited overlay|足够的覆盖空间]] 来更新内核,内核和 initramfs 将会被安装至 /boot 目录。要将它们投入使用,必须将它们移动到安装分区的 /syslinux 目录。该目录可以在运行的 Live USB 文件系统的 /run/initramfs/live 挂载点下面找到。新的 initramfs (例如 initramfs-4.8.1-1.fc25.x86_64.img)和内核(例如 vmlinuz-4.8.1-1.fc25.x86_64)应该被分别移动并替换 /run/initramfs/live/syslinux/initrd0.img 和 /run/initramfs/live/syslinux/vmlinuz0 文件。 | |||
* '''注意''': ''[[dracut]]'' 默认不再包含 ''dmsquash-live'' 模块。从 Fedora 19 开始, ''dracut'' 默认设为 {{command|hostonly="yes"}} 选项,它排除了 ''dmsquash-live'' 模块。因此,可以在更新内核之前,以 root 用户身份添加 dracut 配置文件: | |||
<pre> | |||
echo 'hostonly="no" | |||
add_dracutmodules+=" dmsquash-live " | |||
compress="xz"' > /etc/dracut.conf.d/01-liveos.conf | |||
</pre> | |||
以下命令将新的内核和 initramfs 文件移动到设备的 /syslinux 目录: | |||
<pre> | |||
bootpath=run/initramfs/live/syslinux | |||
new=4.8.1-1.fc25.x86_64 | |||
cd / | |||
mv -f boot/vmlinuz-$new ${bootpath}/vmlinuz0 | |||
mv -f boot/initramfs-${new}.img ${bootpath}/initrd0.img | |||
</pre> | |||
{{admon/note | Fedora 指南 | 本指南中记录的程序也记录在 http://docs.fedoraproject.org/readme-burning-isos/ 。指南中的内容可能与文档不同。如果您在编辑此网页或发现指南有问题,请根据指南提交错误,以便更新其内容。}} | |||
<noinclude> | |||
[ | [[Category:LiveMedia]] | ||
</noinclude> | |||
= 参考 = | = 参考 = | ||
| Line 329: | Line 326: | ||
* http://www.redhat.com/archives/fedora-test-list/2007-May/msg00308.html | * http://www.redhat.com/archives/fedora-test-list/2007-May/msg00308.html | ||
* http://www.redhat.com/archives/fedora-livecd-list/2007-April/msg00029.html | * http://www.redhat.com/archives/fedora-livecd-list/2007-April/msg00029.html | ||
* [http://www.redhatmagazine.com/2007/11/07/i-am-fedora-and-so-can-you/ Red Hat Magazine | I am Fedora, and so can you!] | |||
Revision as of 18:45, 13 October 2016
本页介绍 如何创建并使用 Fedora 启动 U 盘。您可以将 Fedora ISO 镜像 写入 U 盘,在不安装 Fedora 系统到硬盘的情况下启动一台支持 U 盘启动的电脑。您可以在启动U盘中划分一块区域存储对系统的更改(安装软件或修改配置),这种模式称为 持续覆盖。您也可以划分一块单独空间用来存储用户账户信息和数据,比如文档和下载的文件,当然,为了数据安全您可以选择加密它们。总之,因为安装是非破坏性的,之前的文件和剩余的空间都可以在系统中访问。这相当于把整个电脑装在口袋里,在能找到的大部分机器上启动您自己的系统。
在现在的 Fedora 版本中,您也可以把非 Live 版本的 Fedora 镜像(DVD 和网络安装镜像)写入 U 盘,这样比写入光盘更快更方便。
快速开始:使用 Fedora Media Writer
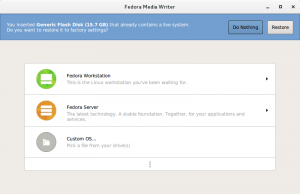
在大多数情况下,创建 Fedora U 盘的最佳工具是 Fedora Media Writer,以前称为 LiveUSB Creator。它目前支持 Fedora(其他发行版使用 Flatpak),Windows 和 macOS。
Fedora Media Writer 图形化工具非常易于使用。它可以下载最新版本的 Fedora 镜像,并将其写入 U 盘。
在 Fedora 中,您可以使用图形化软件安装工具安装 ![]() mediawriter
mediawriter
su -c 'dnf --enablerepo=updates-testing install mediawriter'
在 Windows 和 macOS 中,您可以从 发布页 下载安装包。在其他 Linux 发行版,如果支持 Flatpak 应用分发系统,您可以从 发布页 下载 flatpkg 包。
要运行该工具,请在系统菜单中查找 Fedora Media Writer。当您启动 Fedora Media Writer 时,底部的三个点将闪烁,工具将检查新的 Fedora 版本。
执行以下步骤写入 U 盘:
- 选择您希望安装或试用的 Fedora 版本。
- 在标题页,您可以选择 Workstation, Server 或您的 .iso 文件。其他选项(包括 KDE, Cinnamon, Xfce 等等)在列表底部的 "..." 按钮中。
- 确保您的 U 盘已插入系统。
- 点击 Create Live USB。
- 确保已选择右侧的 U 盘。
- 点击 Write to disk 并等待写入完成。
- 一旦写入完成,关闭系统并从 U 盘启动(参见 引导部分)。
写入后,您的 U 盘分区布局将改变,一些系统可能提示它有 10MB 容量。要将 U 盘恢复出厂设置,请在 Fedora Media Writer 运行时再次插入 U 盘。应用程序将提供恢复出厂设置的选项。恢复后,U 盘将包含一个 VFAT 分区。
系统需求
- 一台使用 GNU/Linux,Windows 或者 MacOS 的电脑。
- 一个拥有 1G 以上存储空间的 USB闪存设备,比如 U 盘、存储卡等 。
- 1 个从 http://fedoraproject.org/get-fedora 下载的镜像文件。
从 USB 设备启动
几乎所有的现代 PC 都支持从 U 盘启动(有些非常老的可能无法启动)。当然,您需要设置从 USB 引导启动系统。首先,您需要按以下步骤操作:
- 关闭计算机。
- 插入 USB 设备。
- 移除所有其他便携式媒体,例如 CD, DVD, 软盘或其他 U 盘。
- 启动计算机。
- 如果计算机配置为从 USB 驱动器自动引导,您将看到屏幕显示 "Automatic boot in 10 seconds..."(如果您的计算机支持 UEFI 引导,这里会显示更多的 最小启动菜单)。
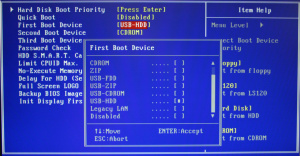
如果计算机正常从硬盘驱动器引导,您需要手动配置 BIOS 从 U 盘驱动器引导。通常,应该按以下步骤操作:
- 等待计算机安全重启。
- 当计算机开始重启时,您需要仔细观察并按下指定按键(通常是 Escape, Tab, F12 或 Delete)进入引导设备选择菜单。如果您错过了,需要重启并重试。
- 进入 "BIOS" 或引导设备选择菜单,将您的 USB 设备设为第一启动项。
- 注意! 如果您修改了其他设置,可能会导致计算机无法启动。建议您记住修改的选项,以备不时之需。
- 保存更改,退出,从 USB 设备引导启动计算机。
如果您的系统基于 UEFI 固件,它通常支持 UEFI 模式和 BIOS 兼容模式。如果您以 UEFI 模式启动并安装 Fedora,Fedora 引导将安装至 UEFI 分区(以 UEFI+GPT 模式启动)。如果您以 BIOS 兼容模式启动并安装 Fedora,Fedora 将以 BIOS+MBR 模式启动。更多信息,请参阅 UEFI 页。使用 Fedora Media Writer, GNOME Disk Utility, dd, 或其他类似 dd 的工具,和 livecd-iso-to-disk 的 --efi 选项将 x86_64 镜像写入 U 盘,U 盘将支持 UEFI 引导。使用其他工具写入 U 盘可能不支持 UEFI 引导,并且 i686 镜像不支持通过 UEFI 引导。
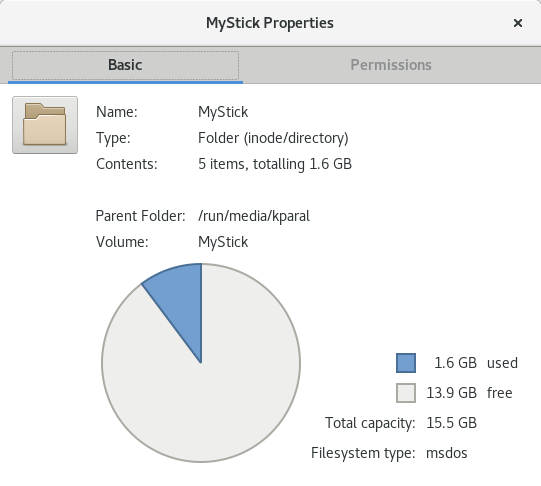
检查 USB 磁盘大小 / 可用空间
如前所述,磁盘必须有一定的存储空间,具体取决于您选择的镜像。如果您使用破坏性方法,U 盘必须至少为镜像大小;如果使用非破坏性方法,它必须至少有足够的可用空间。无论您使用什么操作系统,都可以通过文件管理器检查设备可用空间,通常是右键单击并选择 Properties。以下是 GNOME 文件管理器截图:
您也可以通过执行 df -h 命令查看:
/dev/sdX1 3.9G 4.0K 3.9G 1% /media/usbdisk
确保第一栏大于 1.0G。
在 Linux 上通过 /dev 名称标识设备
大多数 其他写入方法 都需要知道 U 盘的 /dev 设备名称。例如,当使用 Linux 时可能为 /dev/sdc。Fedora Media Writer 不需要用户提供设备名。查找设备名可使用以下步骤:
- 插入 U 盘。
- 打开终端,运行
dmesg。 - 在输出的最后,您会看到类似的信息:
[32656.573467] sd 8:0:0:0: [sdX] Attached SCSI removable disk
其中 sdX(可能是 sdb, sdc, sdd等)标签就是您需要使用的设备名。如果您连接了多个 USB 设备,请务必小心识别设备名,通常输出中会包含制造商名称或容量,可以使用这些来区分多个 USB 设备。记下这个标签,下文我们称之为 sdX。
其他 U 盘写入方法
在大多数情况下,推荐使用 Fedora Media Writer。在本节中,记录了其他有用的工具。
使用 GNOME Disk Utility (Linux, 图形, 破坏性)
此方法适用于已安装 GNOME,Nautilus 和 GNOME Disk Utility 的 Linux(或 *nix)。如果您使用的是不支持 Flatpak 的发行版,这可能是最简单的方法。标准安装的 Fedora 或许多其他基于 GNOME 的发行版,都可以使用此方法。在 Fedora 上,确保已安装 ![]() nautilus
nautilus![]() gnome-disk-utility
gnome-disk-utility
- 下载 Fedora 镜像,插入不包含任何有用数据的 U 盘
- 运行 Nautilus (Files)
- 找到已下载的镜像,右键单击,转到Open With,并点击 Disk Image Writer
- 再次检查 U 盘,确保您真的不需要其中的数据!
- 在 Destination 中选择您的 U 盘,并点击 Start Restoring...
命令行方法:使用 livecd-iso-to-disk 工具 (仅 Fedora, 非图形, 破坏性/非破坏性)
livecd-iso-to-disk 方法的可靠性比 Fedora Media Writer 稍差,只能在 Fedora 中可靠地使用:它不能在 Windows 或 macOS 中使用,且不支持(通常失败)非 Fedora 发行版。但是,它支持 FMW 不支持的三个高级功能:
- 您可以使用 非破坏性 方法创建安装 U 盘,U 盘中的现有文件不会被销毁。该方法没有 破坏性 写入方法可靠,且只在没有 U 盘可用时才使用。
- 写入 Live 镜像时,您可以使用 永久覆盖 功能,它允许在重启后保留之前的更改。您可以定期执行更新,就像使用磁盘中的系统一样。当然,内核更新需要 手动介入;另外,覆盖空间可能不足。不使用 永久覆盖 功能,每次启动时将丢弃之前的更改。
- 在 Live 镜像上,您也可以划分一个独立的区域来存储用户账户信息和数据,例如文档和下载的文件,可选的加密让您的数据更安全。
通过结合这些功能,您可以随身携带您的 Fedora 系统,并在任何计算机中启动。
在旧的 Fedora 系统中使用 livecd-iso-to-disk 写入新系统不是个好主意:
最好只写入一个版本,最多覆盖旧版本不超过两次。
请确保已安装 ![]() livecd-tools
livecd-toolssu -c 'dnf install livecd-tools'
基本示例如下。请注意首先识别您的 U 盘设备名。在所有情况下,您可以添加参数--efi(尝试)以原生 UEFI 模式制作引导 U 盘。更详细的使用信息,请运行:livecd-iso-to-disk --help 或 man livecd-iso-to-disk。
要将现有的 U 盘制作为可启动 U 盘,而不删除其中的任何数据,请确保在执行以下操作前未挂载 USB 驱动器,并在出现提示时输入 root 密码:
su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-41-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"
如果无法从使用上述方法创建的磁盘进行引导,则在重新分区和格式化前,重置为主引导记录:
su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk --reset-mbr Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-41-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"
如果有必要,您可以使用 livecd-iso-to-disk 重新分区和格式化目标设备:
su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk --format --reset-mbr Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-41-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"
使用 --home-size-mb 参数,可以为 /home 划分保留的文件系统。例如:
su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk --home-size-mb 2048 Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-41-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"
这将创建一个 2GiB 文件系统,每次启动 U 盘时挂载为 /home,从而允许您保留 /home 中的数据。
要启用 '数据持久性' 支持(对整个 Live 环境所做的更改将在引导期间持续存在),需要添加 --overlay-size-mb 参数,将持久性数据存储区域添加到目标设备。例如:
su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk --overlay-size-mb 2048 Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-41-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"
其中 2048 是覆盖的期望大小(MB)。对于 VFAT,livecd-iso-to-disk 工具不接受大于 4095 的值;对于 ext[234] 文件系统,只受可用空间的限制。
您可以组合 --home-size-mb 和 --overlay-size-mb,这种情况下写入 /home 的数据不会占用持久覆盖的空间。
命令行 "直接写入" 方法 (多操作系统, 非图形, 破坏性)
此方法直接将镜像写入 U 盘,就像 Fedora Media Writer 或 GNOME Disk Utility,但使用名为 dd 的命令行工具。与其他 “直接写入” 方法一样,它会破坏 U 盘中的所有数据,不支持任何高级功能,如数据持久性,但该方法非常可靠。 dd 工具可用于大多数类 Unix 操作系统,包括 Linux 和 macOS,以及 一个 Windows 版本。如果您不能使用 Fedora Media Writer 或 GNOME 磁盘实用程序,或只是喜欢命令行程序,并想要一个简单/快速的方式写入 U 盘,这就是最好的方法。
- 识别您的 U 盘设备名。如果您使用 Windows,
dd --list命令将显示正确的名称。 - 卸载该设备所有已挂载的分区。 这非常重要,否则写入的镜像可能损坏。您可以使用
umount /dev/sdX*命令卸载所有分区。 - 将 ISO 文件写入设备:
su -c 'dd if=/path/to/image.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=8M status=progress oflag=direct'
- 等待命令完成。
- 如果您看到 dd: invalid status flag: 'progress',您的 dd 版本不支持 status=progress 选项,您需要删除该选项,然后重试(您将不能看到进度条)。
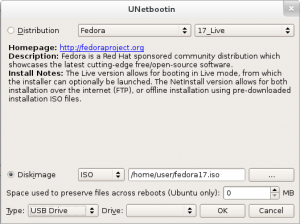
使用 UNetbootin (Windows, macOS 和 Linux, 图形, 非破坏性)
虽然结果可能会有所不同,但通常情况下,使用 Fedora Media Writer, livecd-iso-to-disk, GNOME 和 dd 方法的结果比 UNetbootin 更好。如果您遇到 UNetbootin 的问题,请联系 UNetbootin 开发人员。
UNetbootin 是一个图形化的可引导 U 盘镜像写入工具。它允许您保存 USB 驱动器中的任何数据。如果您在启动时遇到问题,可以尝试使用一个干净的 FAT32 格式的驱动器。
如果您运行的是 64 位 Linux 发行版,UNetbootin 可能无法运行,您需要安装相当多的 32 位系统库。Fedora 无法帮助您:请直接向 UNetbootin 开发人员反馈问题。
- 从 UNetbootin 官方网站 下载最新版本,并安装。在 Linux 中,下载可执行文件,添加可执行权限
chmod ugo+x filename,运行即可。 - 启动 UNetbootin。在 Linux 中,需要输入 root 密码。
- 点击 Diskimage,并选择您下载的 ISO 文件。
- 选择类型:USB 设备和 选择正确的 USB 设备
- 点击确定
从运行的 Live 环境创建安装 U 盘
如果您已运行在 Live CD, DVD, USB 环境。您可以执行以下命令,制作一个可引导 U 盘。
su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk /run/initramfs/livedev /dev/sdX"
在外部挂载根文件系统,请参阅 该节。
故障排除
Fedora Media Writer 问题
- 可以向 GitHub 或 Bugzilla 提交错误报告。
- 您可以 浏览已存在的 Bugzilla 报告。
livecd-iso-to-disk 问题
分区未标记为可引导!
如果您收到消息 Partition isn't marked bootable!,您需要标记分区为可引导。为此,运行 su -c 'parted /dev/sdX',并使用 toggle N boot 命令(N 为分区号)。例如:
$ parted /dev/sdb GNU Parted 1.8.6 Using /dev/sdb Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands. (parted) print # 查看分区信息 Model: Imation Flash Drive (scsi) Disk /dev/sdX: 1062MB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: msdos Number Start End Size Type File system Flags 1 32.3kB 1062MB 1062MB primary fat16 (parted) toggle 1 boot # 标记分区1 为可引导 (parted) print # 查看分区信息 Model: Imation Flash Drive (scsi) Disk /dev/sdX: 1062MB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: msdos Number Start End Size Type File system Flags 1 32.3kB 1062MB 1062MB primary fat16 boot (parted) quit # 退出 Information: Don't forget to update /etc/fstab, if necessary.
分区需要文件系统标签!
如果您收到消息 Need to have a filesystem label or UUID for your USB device,您需要为分区设置标签:su -c "dosfslabel /dev/sdX LIVE"
分区有不同的物理/逻辑结束标记!
如果您从 fdisk 获得该消息,您需要在写入镜像时,使用 --format 参数重新格式化 U 盘。
MBR 显示为空白!
如果测试引导报告损坏的引导扇区,或者您收到消息 MBR appears to be blank.,您需要在写入镜像时,使用 --reset-mbr 选项重设主引导记录(MBR)。
$ su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-{{FedoraVersionNumber|next}}-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"
MBR appears to be blank.
You can add an MBR to this device with
Cleaning up to exit...
重设主引导记录(MBR):
$ su -c "livecd-iso-to-disk --reset-mbr Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-{{FedoraVersionNumber|next}}-1.1.iso /dev/sdX"
在其他 Linux 发行版使用 livecd-iso-to-disk
livecd-iso-to-disk 不能在非 Fedora 系统中运行。即使它在其他发行版可以运行并成功写入 U 盘,该 U 盘也可能无法引导。在其他非 Fedora 发行版上使用 livecd-iso-to-disk 不受支持,无法正常工作:请使用其他方法,例如 Fedora Media Writer。
Ubuntu 的 usb-creator 命令
Ubuntu 及其衍生版有一个 usb-creator 程序,类似于 Fedora Media Writer。它不能用于写入 Fedora ISO 镜像。usb-creator 需要 ISO 具有 Debian 布局,具有 /.disk/info 文件和 casper 目录。不要尝试使用该工具写入 Fedora ISO 镜像。
使用 qemu 测试可引导 U 盘
以下截图展示了,使用 QEMU 测试可引导 U 盘。
例如,使用以下命令测试可引导 U 盘:
su -c 'umount /dev/sdX1' qemu -hda /dev/sdX -m 1024 -vga std
挂载 Live USB 文件系统
您可以尝试使用 ![]() livecd-tools
livecd-tools
为使用 livecd-iso-to-disk 持久覆盖模式写入的镜像更新内核
如果您的 U 盘有 足够的覆盖空间 来更新内核,内核和 initramfs 将会被安装至 /boot 目录。要将它们投入使用,必须将它们移动到安装分区的 /syslinux 目录。该目录可以在运行的 Live USB 文件系统的 /run/initramfs/live 挂载点下面找到。新的 initramfs (例如 initramfs-4.8.1-1.fc25.x86_64.img)和内核(例如 vmlinuz-4.8.1-1.fc25.x86_64)应该被分别移动并替换 /run/initramfs/live/syslinux/initrd0.img 和 /run/initramfs/live/syslinux/vmlinuz0 文件。
- 注意: dracut 默认不再包含 dmsquash-live 模块。从 Fedora 19 开始, dracut 默认设为
hostonly="yes"选项,它排除了 dmsquash-live 模块。因此,可以在更新内核之前,以 root 用户身份添加 dracut 配置文件:
echo 'hostonly="no" add_dracutmodules+=" dmsquash-live " compress="xz"' > /etc/dracut.conf.d/01-liveos.conf
以下命令将新的内核和 initramfs 文件移动到设备的 /syslinux 目录:
bootpath=run/initramfs/live/syslinux
new=4.8.1-1.fc25.x86_64
cd /
mv -f boot/vmlinuz-$new ${bootpath}/vmlinuz0
mv -f boot/initramfs-${new}.img ${bootpath}/initrd0.img