Mirroring
Introduction
The most common nocturnal activity of an engineering student, particularly when exams are approaching, is to fire up a first person shooter game. Now suppose, the geek in you, fed up with all the trivialities a text book has to offer, decide to challenge your friend to a deadly dual of OpenAreana. According to murphy's law, he won't have it installed, and the Internet connection will go down at the very moment. Now being a geek, though you are sure the world is conspiring against you, you won't give up so easily, would you? You will decide to see the end of it by creating a local repository of the Fedora, so that every package is ready to serve when you want them. Of course you will be able to do it yourself, but I consider it my duty to make it easier so to allow you to take up more important duties like running a OpenArena server.
Now, having read so far, if you are not entirely sure what this is all about, let me tell you: it is about mirroring fedora repositories within your organisation or institute. The benefits: considerably low download time, effective use of bandwidth and lowered cost.
According to wikipedia, In computing, a mirror is an exact copy of a data set. On the Internet, a mirror site is an exact copy of another Internet site. When you try to install a new package into your Fedora Installation, either via packagekit or via yum, what they basically do is fetch the packages from an Internet site along with the libraries required for it and install it on your computer. Now softwares like OpenOffice or OpenArena are very big in size and along with all the dependencies, that is the other softwares on which this particular software depends, the download size may be in the order of hundreds of Megabits.
Now consider a simple calculation, if your institute or organisation has 100 users and each downloads OpenOffice separately, it will take around 100x150 = 15000Mb = Apprx.14.5Gbs of bandwidth. If you consider even a normal usage senario, where users occationally install new softwares and updates their system, the download can easily reach the Terabite level per month. In countries like India, where bandwidth is a costly commodity, it is hardly possible for an Institute or Organisations to invest an astronomical amount for such a huge bandwidth and this can easy play a spoilsport to the advent of FOSS.
The easy solution to this problem is to put up a server inside the institute or organisation, where all the contents are downloaded and updated periodically and users can get the software from it instead of the Internet. Considering that the cost of bandwidth inside a LAN is trivial and it usually offers much better throughput, mirroring can be an ideal solution to reduce the expenditure and can considerably speed up installations of new software or updates. It can even reduce the need of a physical media as you can use it for diskless network installations.
In the subsequent sections, I shall take you to a step by step guide on how to make a fedora mirror. Yes, it is easy, but at times it can be puzzling too.
Mirroring Requirements
Hardware
Mirroring does not cost much as far as hardware is concerned. If you are going to mirror the whole fedora content, it may take you over a Terabite of disk space. But if you are not an ISP or a big educational institute, you probably won't need all the contents available. It should be an amicable solution for most of the organisations to keep 32 bit and 64 bit repositories of last two releases along with the updates. For example, if you are mirroring right now, it would be good to keep 32 bit (generally called as x86) and 64 bit (called as x86_64) Fedora 10 and 11 along with their updates.
A server with approximate 250Gbs of Hard disk space, though the actual need will depend upon the content you want to keep, and 2-4Gbs of RAM should do perfectly.
Software
Software requirement is also minimal. All you need is an apache web server or a ftp server. However, please check your httpd version using httpd -v. If the version is 1.x or 2.0, you will need both the apache and ftp server. This is because earlier apache servers cannot handle files over 2Gbs. However, if you are using apache 2.1 or 2.2, you need not worry about this as large file handling support has been added in these versions of apache. Here, we will show mirroring only using httpd. Mirroring using ftp is almost similar and need no remarkably different configuration.
Bandwidth
The most essential requirement for mirroring is bandwidth. How long your download will take depends on the available bandwidth. Mirroring over a 5Mbps leased line may take well over a couple of days for each release being mirrored. But most of these contents need to be downloaded only once. The subsequent downloads will need much less bandwidth, often as minimal as a couple of hundred Megabits.
If you are trying to be listed as a public mirror of Fedora, by which you want to offer downloads outside your organisation, the official bandwidth requirement is 100Mbps. However, in countries like India, where the number of public mirror is much less than what is required, it is often relaxed. The first public Fedora Mirror in India used to run on a 5Mbps lease line, until other institutes like NIT-H, IIT-M and IIT-K stepped in.
What to mirror?
Though in the previous section I have already suggested that you may choose to mirror the last two releases along with their updates, it obviously depends upon you. The complete list of directories along with their sizes are given at http://download.fedora.redhat.com/pub/DIRECTORY_SIZES.txt . You can choose what to mirror and what not depending upon your organisational or institutional needs.
Public or Private
The first step is to decide if you want to make it a public mirror, which will serve contents to people outside your organisation or not. On the other hand, private mirrors will serve only inside your organisations and the requests coming from your organisations. If you don't have large bandwidth, at least ~100Mbps, it is better to go for a private mirror. However, for countries like India, where the number of mirrors are far less than required, you can go public with 15-20 Mbps bandwidth.
Mirroring Procedure
Synchronising Content
As this is the most time consuming process, it is suggested that you first get this started and while it pulls content from the server, you do other necessary configurations. The only reliable way to do mirroring is to use rsync , which is an utility to for incremental file transfer. Like ftp, rsync also transers file between server and client. But if the file transfer breaks down midway as a result of a network or power outage, it will resume transferring files from the point where it left. It won't start over from the beginning. From now on, we shall use the term "synchronise" instead of "file transfer".
Suppose you want to serve the content from http root directory, i.e., /var/www/html. So first, you change to that directory. Then you create a exclude.txt file. You may put any expression into that file and when rsync is told about it, rsync won't pull those contents.
# cd /var/www/html # touch exclude.txt
An exclude.txt (you can put in any name you like, it may be exclude, exclude.dat or whatever) file typically look like this:
# vi exclude.txt
As you can see you can put in regular expressions into the exclude file. It means, you need not put in all the names of the directories. When you put ppc*, all directories starting with ppc will be excluded.
Now we are ready to pull in the actual content. The rsync command may look like this
# rsync -vaH --exclude-from=path_to_exclude_file --numeric-ids --delete --delete-after --delay-updates rsync://mirror.anl.gov/fedora/linux/releases/11 /var/www/html/
This command will start pulling Fedora 11 repository and put them into /var/www/html/, the root of the webserver.
Now let's see what does this mean. Rsync, as stated earlier, is an incremental file transfer protocol. -v stands for verbose mode, i.e., it will print the outputs in the console while running. -a means achieving option, -H means the rsync run will preserve hard links between the files. Then we define which directories not to synchronise using --exclude-from. the --delete, --delete-after --delay update tells rsync not to delete old contents while synchronising new data. Instead, it tells rsync to keep the old file and directories until the synchronisation is complete. Then we define the remote rsync server and lastly the destination directory.
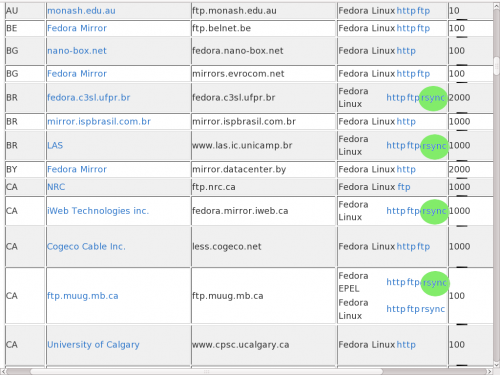
You can get list of servers, which provide rsync service, from the fedora mirrorlist at http://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/publiclist/ .
Saving some bandwidth
A little trick can save you around a few Gigabits of Download. If you are not sure about the directory structure Fedora repositories have, be a bit careful about this.
The iso of Fedora DVD resides at Fedora/$architecture/iso/ directory. Also the same contents of the DVD is at Fedora/$architecture/os/, but as extracted files and directories. For example, http://118.102.181.66/releases/11/Fedora/i386/os/ contains the files of http://118.102.181.66/releases/11/Fedora/i386/iso/Fedora-11-i386-DVD.iso. So if you download the .iso file first and then copy the content over to the os/ directory, you need not download the same content twice. Lets see how do we do it.
Once the download of the DVD iso file is completed, mount it somewhere.
# mount /var/www/html/releases/11/Fedora/i386/iso/Fedora-11-i386-DVD.iso /mnt -o loop # cp -prv /mnt/* /var/www/html/releases/11/Fedora/i386/os/ # umount /mnt
Similarly, you can repeat for x86_64 DVD iso, is you are mirroring that architecture too.
If download stops
In the course of synchronising, you may receive a few messages like this: Suddenly the Dungeon collapses!! - You die.... Don't panic. Only the rsync has stopped for some reason. Just press the up arrow and enter the same command. Rsync will pick up from where it left.
Other Configurations
Let the rsync run in its own course. You have nothing to do other than periodically checking if it has stopped. In the meantime, let's do other necessary configurations.
Configuring Apache server
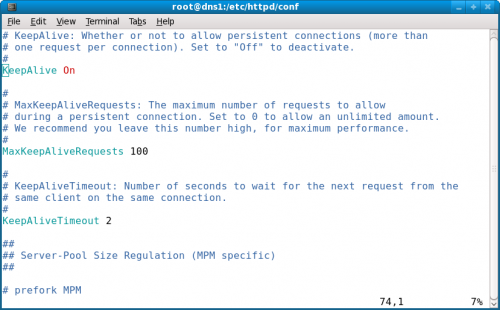
Enable Keepalives
Enabling KeepAlive in httpd allows persistent connections. These long-lived HTTP sessions allow multiple requests to be send over the same TCP connection, and as it does not require seperate connection setup for each file. So this reduces some overhead and significantly reduces latency times. By default, Fedora's Apache httpd package has keepalives disabled. They should be enabled, with a timeout of 2 seconds. Don't keep this very high, it may overload your server.
Handling of metadata
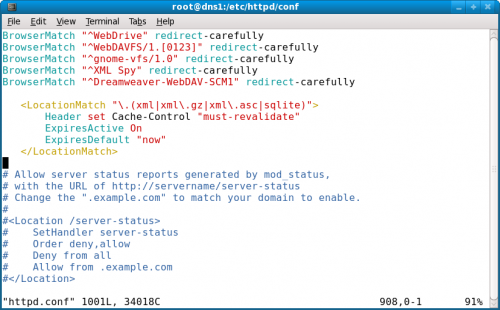
Metadata are typically defined as "data about data". When you try to install a package or update a system, first things which get downloaded is package metadata. These are files with several informations about the packages, their age and other details. Now, for example, if a computer has old metadata cached, according to which all the packges are up-to-date, no new updates will be installed into the system. To work around this, we explicitely add Cache Control: must-revalidate option which insists that yum must revalidate the metadata against the server before serving it from cache. For this, add the following section to your /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf around the <Location> directive (around line 900).
<LocationMatch "\.(xml|xml\.gz|xml\.asc|sqlite)">
Header set Cache-Control "must-revalidate"
ExpiresActive On
ExpiresDefault "now"
</LocationMatch>
Content Types
ISO and RPM files should be served using MIME Content-Type: application/octet-stream. In Apache, this can be done inside a VirtualHost or similar section:
<VirtualHost *:80> AddType application/octet-stream .iso AddType application/octet-stream .rpm </VirtualHost>
Limiting Download Accelerators
Download accelerators will try to open the same file many times, and request chunks, hoping to download them in parallel. This can overload heavily loaded mirror servers, and cause a denial of service.
To limit connections to ISO dirs by some amount per IP:
<IfModule mod_limitipconn.c> MaxConnPerIP 3 </IfModule>
To block ranged requests as this is what download accelerators do indeed:
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Range} [0-9] $
RewriteRule \.iso$ / [F,L]
Restart Apache
Now restart apache. If everything is fine, you should not get an error. If you can start the apache server successfully, it means you are done with most of the things.
Registering your mirror
Now that your configuratin is almost done, you must register your mirror, regardless it is a private mirror or a public mirror.
Get a Fedora Account
Firstly, you need to go to https://admin.fedoraproject.org/accounts/ and get yourself a Fedora account. Without this, you can not prceed further. However, you may not choose to sign the CLA, which is not required if you want to be a mirror-admin only.
Register your Mirror
At this point, let me introduce MirrorManager, which automatically keeps track of the mirrors. Go to https://admin.fedoraproject.org/mirrormanager/ and login with the credentials you just created. Here you need to do only two things.
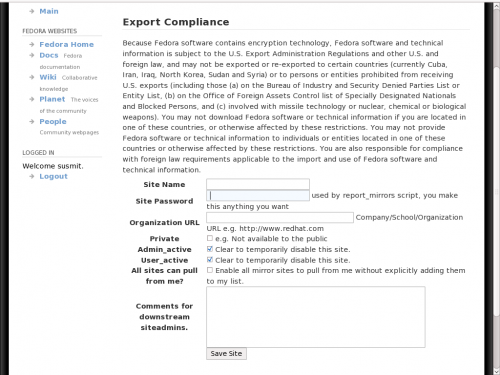
First, create a site using the link [Add Site] under My Sites and Hosts. What you need to put into the fields are explained besides the fields and are self-explanatory.
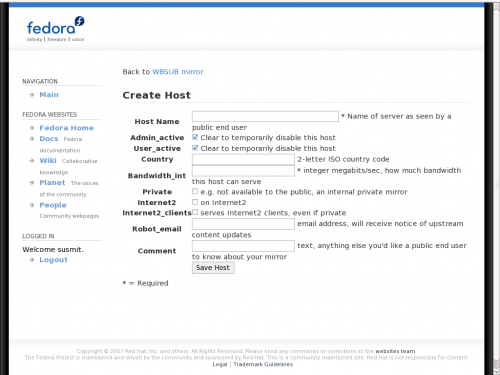
Once you fill in the form and save the site, you will find a new link My Hosts. Now add a host to it. The difference between host and site is: a site is the details of the parent organisation, while host is the details of the individual machines hosting the repository. A site can have multiple hosts.
You can restrict your mirror within the organisation using the Private checkbox. Once you save the host, you will have a few more options to fine tune your mirror. They are well described and need not be told here.
Run report_mirror
Now, your site and the host is created, it is time to automatically update the mirrormanager about your mirror contents. For this, there is a script called report_mirror which, when run, automatically updates the contents of your mirror to mirrormanager database. For this, you need to install mirrormanager-client. You can do it very easily using:
# yum -y install mirrormanager-client
You need to edit a configuration file minimally. Once the installation is done, you will find the configuration file under /etc/mirrormanager-client. Edit it suitably to reflect the contents and the paths of your mirror.
[global] # if enabled=0, no data is sent to the database enabled=1 server=https://admin.fedoraproject.org/mirrormanager/xmlrpc
[site] # if enabled=0, no data about this site is sent to the database enabled=1 name=WBSUB mirror password=*****
[host] # if enabled=0, no data about this host is sent to the database enabled=1 name=118.102.181.66
[Fedora Linux] enabled=1 path=/var/www/html/ replace this with your path_to_content
You will find more categories under this. If you have these contents, set enabled=1 or set enabled=0. You can also delete them without problem.
Once this far is done, run report_mirror script using
/usr/bin/report_mirror -c /etc/mirrormanager-client/report_mirror.conf
Once successfully completed, it will show "Checked in successfully". You can now see the contents of your mirror under your mirrormanager host. Put it into a cron so that it can periodically update the mirrormanager database.
Subscribe to Mailing Lists
To be notified about the releases and other details, you should subscribe to http://www.redhat.com/mailman/listinfo/mirror-list and http://www.redhat.com/mailman/listinfo/mirror-list-d, which is a discussion list.